¿Qué es la Automatización de Procesos?
La automatización de procesos consiste en el uso de tecnología para ejecutar tareas repetitivas o procesos de negocio con intervención humana mínima. Permite a las empresas optimizar sus operaciones, reducir errores, ahorrar tiempo y recursos, y mejorar la experiencia tanto de empleados como de clientes.
La automatización de procesos permite:
- Reducir el tiempo dedicado a tareas repetitivas y de bajo valor añadido
- Minimizar errores humanos y mejorar la precisión
- Aumentar la productividad y eficiencia operativa
- Reducir costes operativos y administrativos
- Mejorar la experiencia de cliente y empleado
- Obtener datos valiosos para la toma de decisiones
Tipos de Automatización de Procesos
RPA (Robotic Process Automation)

Tecnología que permite configurar software o "robots" para capturar e interpretar aplicaciones existentes, procesar transacciones, manipular datos, desencadenar respuestas y comunicarse con otros sistemas digitales.
Aplicaciones: procesamiento de facturas, gestión de pedidos, entrada de datos, conciliación financiera, onboarding de clientes, generación de informes.
BPM (Business Process Management)
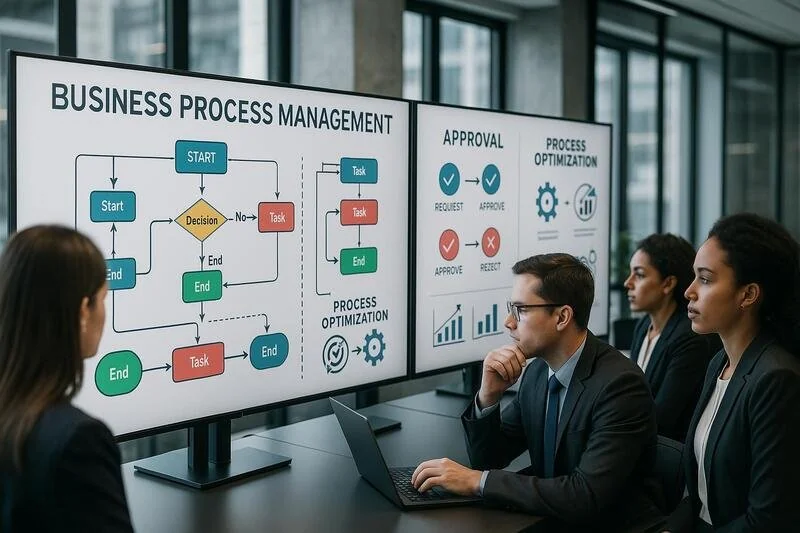
Disciplina que combina modelado, automatización, ejecución, control, medición y optimización de flujos de trabajo empresariales para apoyar los objetivos de la empresa, abarcar sistemas, empleados, clientes y socios.
Aplicaciones: gestión de aprobaciones, procesos de compra, gestión de reclamaciones, procesos de contratación, gestión documental.
Workflow Automation

Tecnología que utiliza reglas definidas para transferir tareas, información o documentos de un participante a otro para su acción, según un conjunto de reglas de procedimiento.
Aplicaciones: aprobaciones de documentos, gestión de tareas, notificaciones automáticas, seguimiento de proyectos, procesos de onboarding.
Integración de Aplicaciones
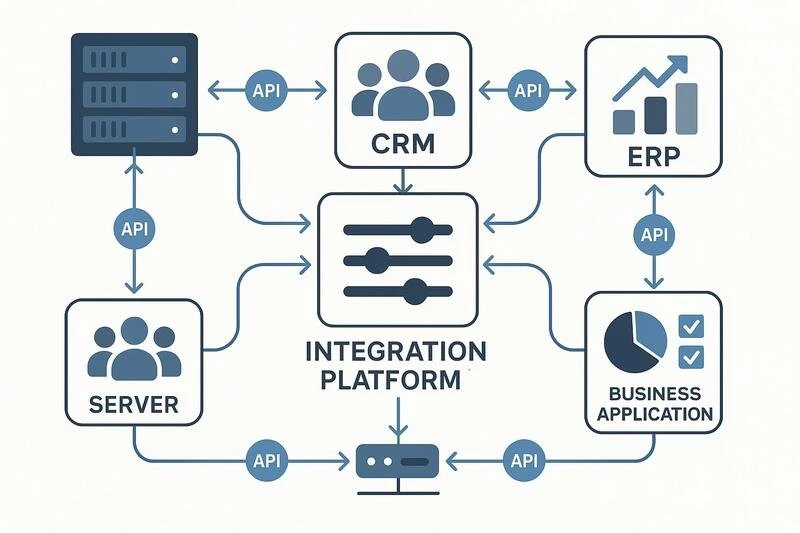
Proceso de conectar diferentes aplicaciones de software para que funcionen juntas y compartan datos, eliminando silos de información y automatizando el flujo de datos entre sistemas.
Aplicaciones: sincronización de datos entre CRM y ERP, integración de e-commerce con sistemas de inventario, conexión de herramientas de marketing con ventas.
Beneficios de la Automatización de Procesos
Ahorro de Tiempo
Reducción significativa del tiempo dedicado a tareas repetitivas, permitiendo a los empleados centrarse en actividades de mayor valor añadido.
Reducción de Costes
Disminución de costes operativos y administrativos al optimizar procesos y reducir la necesidad de intervención manual.
Mayor Precisión
Eliminación de errores humanos en tareas repetitivas, mejorando la calidad y consistencia de los resultados.
Escalabilidad
Capacidad para gestionar volúmenes crecientes de trabajo sin necesidad de aumentar proporcionalmente los recursos humanos.
Mejor Experiencia
Mejora de la experiencia de clientes y empleados gracias a procesos más rápidos, eficientes y con menos fricciones.
Insights Valiosos
Obtención de datos y métricas precisas sobre los procesos, facilitando la toma de decisiones basada en datos.
¿Cómo Implementar la Automatización de Procesos?
Identificación de Procesos
Análisis y selección de los procesos candidatos para automatización, priorizando aquellos repetitivos, basados en reglas, con alto volumen y propensos a errores.
Documentación de Procesos
Mapeo detallado de los procesos actuales, identificando entradas, salidas, reglas de negocio, excepciones y puntos de decisión.
Selección de Herramientas
Evaluación y selección de las tecnologías de automatización más adecuadas para los procesos identificados (RPA, BPM, workflow, etc.).
Desarrollo e Implementación
Configuración, desarrollo y despliegue de las soluciones de automatización, incluyendo pruebas exhaustivas y gestión del cambio.
Formación
Capacitación de los usuarios y administradores en el uso y mantenimiento de las soluciones de automatización implementadas.
Monitorización y Optimización
Seguimiento continuo del rendimiento de los procesos automatizados e implementación de mejoras para optimizar resultados.